|
|
The
University of Queensland
|

Aims
1. The development of a technology for demonstrating fundamental gate operations relevant to the Kane quantum computer using optical diagnostics of quantum dot systems.
2. The investigation of methods for optically detecting the spin-state of a single electron (Qubit) on a phosphorus donor in silicon.
Quantum Dots for Quantum Computation
The J-gate operation of the Kane quantum computer uses an electric field to control the wavefunction overlap between two neighbouring electrons bound to phosphorus donor sites in silicon. Electron wavefunction overlap can also be created in quantum dots. Using standard optical diagnostics we hope to study J-gate interaction.
| Quantum dots grown using colloidal synthesis can be dried into thin films. The application of the colloidal solution containing the polymer to a metal nano-mask consisting of an array of sub-micron holes allows near-field detection of any quantum dots that lie directly under a hole.While the distribution of quantum dots in the film is random, variation of the quantum dot density is easily achieved by dilution, enabling an optimum density for the mask hole size to be found. | 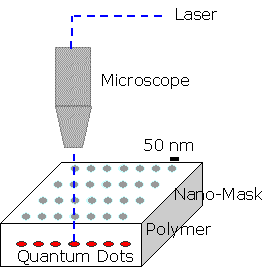 |
If two or more quantum dots lie under a hole in the mask, they will be detected spectroscopically. The use of a metal nano-mask for this near-field detection enables the mask to be charged, which inturn will apply an electric field to the quantum dots under observation. The application of such an electric field will provide a means of continuously varying the coupling between quantum dots, which is effectively the J-gate operation.
 |